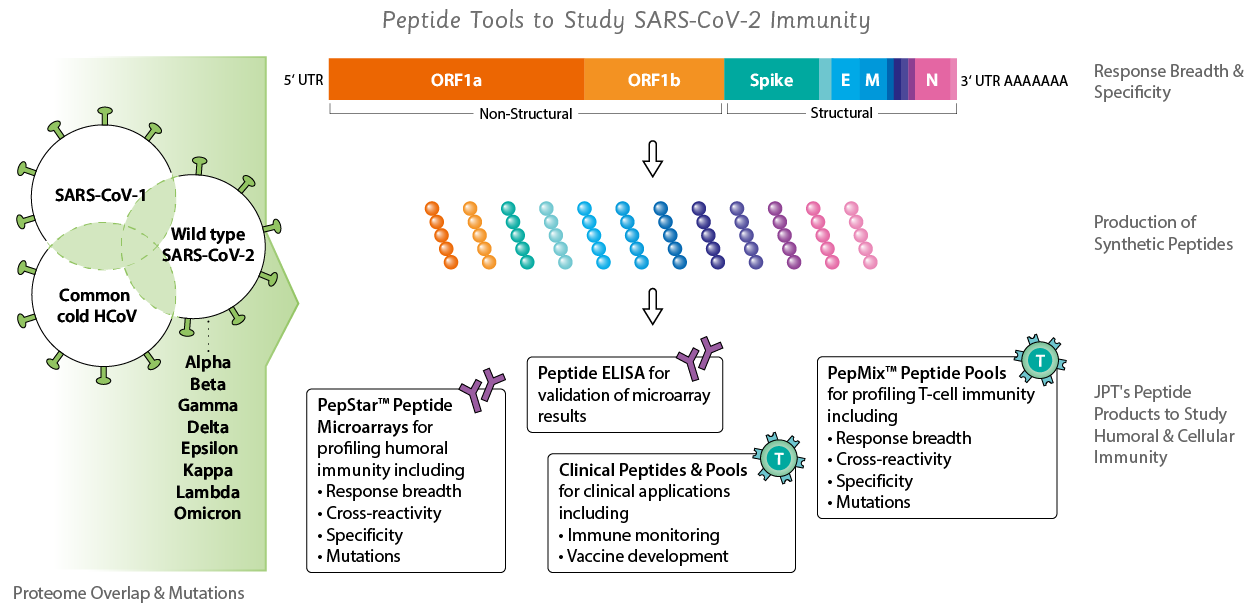
Peptide Tools to Study SARS-CoV-2
JPT has launched a broad development program to provide access to genome spanning SARS-CoV-2 peptide tools and its different mutation variants for applications such as:- SARS-CoV-2 clinical trial immune monitoring
- SARS-CoV-2 evaluation of cross reactivities
- SARS-CoV-2 blood and sero test development
- SARS-CoV-2 T-and B-cell epitope discovery
We have broadened our portfolio of coronavirus related products beyond SARS-CoV-2, including SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and common cold viruses CoV 229E, OC43, HKU1 and NL63. Have a look below!
Overview of Spike Glycoprotein Mutations Flyer: Covid-19 Peptide Tools
JPT's SARS-CoV-2 Peptide Formats
Cellular Immunity
PepMix™ Peptide Pools
- Antigen-specific T-cell stimulation
- Cellular immune monitoring
- Vaccine target discovery
- Blood test development
- Cross reactivity testing (SARS-CoV-2 vs. SARS, MERS, HCoV 229E, OC43…)
- Cell therapy development
- Efficient epitope mapping and identification
- Matrix Pools and individual peptides spanning a whole antigen in one set
- Minimal sample amount required
- Antigen specific T-cell stimulation in T-cell assays (i.e. ELISpot, ICS)
- Immune monitoring
- Proliferation assays
- T-cell expansion
Humoral Immunity
PepStar™ Peptide Microarrays
- Humoral immune monitoring
- Antibody epitope discovery
- Cross reactivity testing (SARS-CoV-2 vs. SARS, MERS, HCoV 229E, OC43…)
- Seromarker discovery
- PepStar™ Antigen Collection Pan-Coronavirus for cross reactivity testing with SARS-CoV-2 vs. SARS, MERS, HCoV 229E, OC43…)
- PepStar™ Peptide Microarrays for individual SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV antigens
- Custom PepStar™ Peptide Microarrays
You define content and layout, we provide economic and fast production in our regulated clean-room environment. We also offer our assay and analysis service using your samples with your tailored peptide microarray.
- Thousands of peptides spanning the entire SARS-CoV-2 genome using smallest sample volumes
- Incubation using smallest sample volumes
- Study of antibody cross-reactivities between SARS-CoV-2 and other corona viruses
- Verification of peptide binders with a large numbers of samples
- Transfer of results to ELISA platform for rapid test development
- Peptide ELISA development and service using SARS-CoV-2 peptides or a combination with other corona viruses
- ELISA-based validation service of peptide binders identified by using JPT’s peptide microarray platform
- Collaborative ELISA test development
Clinical Immune Monitoring & Cell Therapy
Clinical Grade Peptides & PepMix™ Peptide Pools
- High quality chemically synthesized antigen source for vaccine trial monitoring
- Ancillary reagents for cellular therapy development
- Full analytical coverage, stability testing, batch documentation and more
Proteomics
SpikeMix™ SARS-CoV-2
- Identify SARS CoV-2 antigens from biological samples
- Mass spectrometry based assays (MRM)
- Screen 23 proteotypic peptides from SARS-CoV-2
Loading...
Find SARS-CoV-2 Peptide variants
Alpha B.1.1.7
WHO Designation
Variant of Concern
Variant of Concern
First Publication
Investigation of novel SARS-COV-2 variant: Variant of Concern
Chand et al, Public Health England (2020)
Investigation of novel SARS-COV-2 variant: Variant of Concern
Chand et al, Public Health England (2020)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_601443
EPI_ISL_581117
EPI_ISL_601443
EPI_ISL_581117
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.1.7 / Alpha) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.1.7 / Alpha) Spike receptor binding domain
PepStar SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein Variant Collection (incl. Omicron)
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.1.7 / Alpha) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.1.7 / Alpha) Spike receptor binding domain
PepStar SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein Variant Collection (incl. Omicron)
Mutations:
H0069-; V0070-; Y0144-; N0501Y; A0570D; D0614G; P0681H; T0716I; S0982A; D1118H
These mutations characterize approx. 86.8 % of all sequences in the B.1.1.7 lineage. Variants pertaining to Alpha may include these additional mutations:
L0005F, V0006A, S0012F, L0018F, T0020I, R0021T, T0022I, H0049Y, A0067S, A0067V, S0071F, T0076I, P0082L, S0094F, T0095I, E0096D, S0098F, R0102I, D0138H, V0143F, H0146Q, S0151G, W0152R, L0176F, E0180G, R0214L, D0215Y, L0216F, S0221L, A0222V, H0245Y, S0255F, G0261A, A0262-, D0287G, V0289I, T0299I, T0307I, V0308L, T0323I, N0354D, N0394Y, A0475V, E0484K, S0494P, T0572I, A0575S, E0583D, V0622F, A0623S, A0626T, S0640F, Q0675H, Q0677H, T0678I, S0680F, P0681R, A0688V, A0701V, A0706V, T0732I, M0740V, R0765C, P0812S, I0818V, A0831V, K0835R, A0879V, A0892V, I0909V, L0938F, S0939F, G0946V, A1020V, V1129I, E1188D, K1191N, I1227M, V1228L, M1237I, C1243F, P1263L
H0069-; V0070-; Y0144-; N0501Y; A0570D; D0614G; P0681H; T0716I; S0982A; D1118H
These mutations characterize approx. 86.8 % of all sequences in the B.1.1.7 lineage. Variants pertaining to Alpha may include these additional mutations:
L0005F, V0006A, S0012F, L0018F, T0020I, R0021T, T0022I, H0049Y, A0067S, A0067V, S0071F, T0076I, P0082L, S0094F, T0095I, E0096D, S0098F, R0102I, D0138H, V0143F, H0146Q, S0151G, W0152R, L0176F, E0180G, R0214L, D0215Y, L0216F, S0221L, A0222V, H0245Y, S0255F, G0261A, A0262-, D0287G, V0289I, T0299I, T0307I, V0308L, T0323I, N0354D, N0394Y, A0475V, E0484K, S0494P, T0572I, A0575S, E0583D, V0622F, A0623S, A0626T, S0640F, Q0675H, Q0677H, T0678I, S0680F, P0681R, A0688V, A0701V, A0706V, T0732I, M0740V, R0765C, P0812S, I0818V, A0831V, K0835R, A0879V, A0892V, I0909V, L0938F, S0939F, G0946V, A1020V, V1129I, E1188D, K1191N, I1227M, V1228L, M1237I, C1243F, P1263L
Beta B.1.351
WHO Designation
Variant of Concern
Variant of Concern
First Publication
Emergence and rapid spread of a new severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) lineage with multiple spike mutations in South Africa
Tegally et al, Medrxiv (2020)
Emergence and rapid spread of a new severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) lineage with multiple spike mutations in South Africa
Tegally et al, Medrxiv (2020)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_700428
EPI_ISL_700428
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.351 / Beta) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.351 / Beta) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.351 / Beta) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.351 / Beta) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
Mutations:
D0080A, D0215G, L0242-, A0243-, L0244-, K0417N, E0484K, N0501Y, D0614G, A0701V This variant is annotated in the GISAID database 2008 times. An additional variant with the L18F mutation is described 1769 times. (June 13, 2021)
D0080A, D0215G, L0242-, A0243-, L0244-, K0417N, E0484K, N0501Y, D0614G, A0701V This variant is annotated in the GISAID database 2008 times. An additional variant with the L18F mutation is described 1769 times. (June 13, 2021)
Gamma P.1
WHO Designation
Variant of Concern
Variant of Concern
First Publication
Brief report: New Variant Strain of SARS-CoV-2 Identified in Travelers from Brazil National Institute of Infectious Diseases Japan (2021)
Brief report: New Variant Strain of SARS-CoV-2 Identified in Travelers from Brazil National Institute of Infectious Diseases Japan (2021)
JPT's products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike P.1 / Gamma) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD P.1 / Gamma) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike P.1 / Gamma) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD P.1 / Gamma) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
Mutations:
L0018F, T0020N, P0026S, D0138Y, R0190S, K0417T, E0484K, N0501Y, D0614G, H0655Y, T1027I, V1176F
L0018F, T0020N, P0026S, D0138Y, R0190S, K0417T, E0484K, N0501Y, D0614G, H0655Y, T1027I, V1176F
Delta B.1.617.2
WHO Designation
Variant of Concern
Variant of Concern
First Publication
Convergent evolution of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations, L452R, E484Q and P681R, in the second wave of COVID-19 in Maharashtra, India.
Cherian et al, BioRxiv (2021)
Convergent evolution of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations, L452R, E484Q and P681R, in the second wave of COVID-19 in Maharashtra, India.
Cherian et al, BioRxiv (2021)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_1969243
EPI_ISL_1969243
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.617.2 / Delta) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.617.2 / Delta) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.617.2 / Delta) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.617.2 / Delta) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
Mutations:
T0019R; G0142D, E0156-, F0157-, R0158G, L0452R, T0478K, D0614G, P0681R, D0950N
T0019R; G0142D, E0156-, F0157-, R0158G, L0452R, T0478K, D0614G, P0681R, D0950N
Epsilon B.1.429
WHO Designation
Formerly Monitored Variant
Formerly Monitored Variant
First Publication
Emergence of a Novel SARS-CoV-2 Variant in Southern California.
Zhang et al, JAMA (2021)
Emergence of a Novel SARS-CoV-2 Variant in Southern California.
Zhang et al, JAMA (2021)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_755187
EPI_ISL_755187
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.429 / Epsilon) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.429 / Epsilon) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.429 / Epsilon) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.429 / Epsilon) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
Mutations:
S0013I, W0152C, L0452R, D0614G
S0013I, W0152C, L0452R, D0614G
Kappa B.1.617.1
WHO Designation
Formerly Monitored Variant
Formerly Monitored Variant
First Publication
Convergent evolution of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations, L452R, E484Q and P681R, in the second wave of COVID-19 in Maharashtra, India.
Cherian et al, BioRxiv (May 2021)
Convergent evolution of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations, L452R, E484Q and P681R, in the second wave of COVID-19 in Maharashtra, India.
Cherian et al, BioRxiv (May 2021)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_1372093
EPI_ISL_1372093
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.617.1 / Kappa) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.617.1 / Kappa) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.617.1 / Kappa) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.617.1 / Kappa) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
Mutations:
T0095I, G0142D, E0154K, L0452R, E0484Q, D0614G, P0681R, Q1071H
T0095I, G0142D, E0154K, L0452R, E0484Q, D0614G, P0681R, Q1071H
Lambda C.37
WHO Designation
Variant of Interest
Variant of Interest
First Publication
COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update. Edition 44 (2021)
COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update. Edition 44 (2021)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_2158693
EPI_ISL_2158693
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD C.37 / Lambda) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike C.37 / Lambda) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD C.37 / Lambda) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike C.37 / Lambda) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
Mutations:
G0075V; T0076I; RSYLTPGD0246-0253N (R0246-; S0247-; Y0248-; L0249-; T0250-; P0251-; G0252-; D0253N); L0452Q; F0490S; D0614G; T0859N
G0075V; T0076I; RSYLTPGD0246-0253N (R0246-; S0247-; Y0248-; L0249-; T0250-; P0251-; G0252-; D0253N); L0452Q; F0490S; D0614G; T0859N
Omicron B.1.1.529
WHO Designation
Variant of Concern
Variant of Concern
First Publication
Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern
Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_6752027
EPI_ISL_6752027
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (NCAP B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (VEMP B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (VME1 B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Spike receptor binding domain
Multiwell PepStar SARS-COV-2 (Spike) Wild type + Omicron Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (NCAP B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (VEMP B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (VME1 B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein
Mutations:
A0067V; H0069del; V0070del; T0095I; G0142D; V0143del; Y0144del; Y0145del; N0211I*; L0212V*; V0213R*; R0214EPE*; G0339D; S0371L; S0373P; S0375F; K0417N; N0440K; G0446S; S0477N; T0478K; E0484A; Q0493R; G0496S; Q0498R; N0501Y; Y0505H; T0547K; D0614G; H0655Y; N0679K; P0681H; N0764K; D0796Y; N0856K; Q0954H; N0969K; L0981F
A0067V; H0069del; V0070del; T0095I; G0142D; V0143del; Y0144del; Y0145del; N0211I*; L0212V*; V0213R*; R0214EPE*; G0339D; S0371L; S0373P; S0375F; K0417N; N0440K; G0446S; S0477N; T0478K; E0484A; Q0493R; G0496S; Q0498R; N0501Y; Y0505H; T0547K; D0614G; H0655Y; N0679K; P0681H; N0764K; D0796Y; N0856K; Q0954H; N0969K; L0981F
Omicron BA.2
WHO Designation
Variant of Concern
Variant of Concern
First Publication
Virological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2 variant & BA.5 in South Africa
Yamasoba et al., (2022)
Virological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2 variant & BA.5 in South Africa
Yamasoba et al., (2022)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_8459223
EPI_ISL_8459223
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.1.529 / BA.2 / Omicron) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.1.529 / BA.2 / Omicron) Spike receptor binding domain
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (NCAP B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein of Omicron BA.1; (1 aa difference to BA.2)
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (VEMP B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein of Omicron BA.1; (no difference)
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (VME1 B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein of Omicron BA.1; (1 aa difference to BA.2)
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.1.529 / BA.2 / Omicron) Entire spike protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.1.529 / BA.2 / Omicron) Spike receptor binding domain
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (NCAP B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein of Omicron BA.1; (1 aa difference to BA.2)
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (VEMP B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein of Omicron BA.1; (no difference)
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (VME1 B.1.1.529 / Omicron) Entire protein of Omicron BA.1; (1 aa difference to BA.2)
Mutations:
T0019I; L0024-; P0025-; P0026-; A0027S; G0142D; V0213G; G0339D; S0371F; S0373P; S0375F; T0376A; D0405N; R0408S; K0417N; N0440K; S0477N; T0478K; E0484A; Q0493R; Q0498R; N0501Y; Y0505H; D0614G; H0655Y; N0679K; P0681H; N0764K; D0796Y; Q0954H; N0969K
T0019I; L0024-; P0025-; P0026-; A0027S; G0142D; V0213G; G0339D; S0371F; S0373P; S0375F; T0376A; D0405N; R0408S; K0417N; N0440K; S0477N; T0478K; E0484A; Q0493R; Q0498R; N0501Y; Y0505H; D0614G; H0655Y; N0679K; P0681H; N0764K; D0796Y; Q0954H; N0969K
Omicron BA.4/5
WHO Designation
Variant of Concern
Variant of Concern
First Publication
CEmergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineages BA.4 & BA.5 in South Africa
Tegally et al., (2022)
CEmergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineages BA.4 & BA.5 in South Africa
Tegally et al., (2022)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_12688263
EPI_ISL_12688263
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.1.529 / BA.4/5 / Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.1.529 / BA.4/5 / Omicron) Spike Receptor Binding Domain
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike B.1.1.529 / BA.4/5 / Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD B.1.1.529 / BA.4/5 / Omicron) Spike Receptor Binding Domain
Mutations:
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, H0069-, V0070-, G0142D, V0213G, G0339D, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, L0452R, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486V, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, H0069-, V0070-, G0142D, V0213G, G0339D, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, L0452R, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486V, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
Omicron BA.2.75
WHO Designation
Variant under Monitoring
Variant under Monitoring
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_13392500
EPI_ISL_13392500
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike BA.2.75 / Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD BA.2.75 / Omicron) Spike Receptor Binding Domain
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike BA.2.75 / Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD BA.2.75 / Omicron) Spike Receptor Binding Domain
Mutations:
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, G0142D, K0147E, W0152R, F0157L, I0210V, V0213G, G0257S, G0339H, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, G0446S, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, G0142D, K0147E, W0152R, F0157L, I0210V, V0213G, G0257S, G0339H, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, G0446S, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
Omicron BA.2.75.2
WHO Designation
Variant under Monitoring
Variant under Monitoring
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_15104931
EPI_ISL_15104931
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike BA.2.75.2 / Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD BA.2.75.2 / Omicron) : Spike Receptor Binding Domain
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike BA.2.75.2 / Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD BA.2.75.2 / Omicron) : Spike Receptor Binding Domain
Mutations:
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, G0142D, K0147E, W0152R, F0157L, I0210V, V0213G, G0257S, G0339H, R0346T, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, G0446S, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486S, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K, D1199N
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, G0142D, K0147E, W0152R, F0157L, I0210V, V0213G, G0257S, G0339H, R0346T, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, G0446S, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486S, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K, D1199N
Omicron BF.7
WHO Designation
Variant under Monitoring
Variant under Monitoring
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_13183136
EPI_ISL_13183136
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike BF.7/ Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD BF.7 / Omicron) Spike Receptor Binding Domain
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike BF.7/ Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD BF.7 / Omicron) Spike Receptor Binding Domain
Mutations:
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, H0069-, V0070-, G0142D, V0213G, G0339D, R0346T, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, L0452R, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486V, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, H0069-, V0070-, G0142D, V0213G, G0339D, R0346T, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, L0452R, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486V, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
Omicron BQ.1.1
WHO Designation
Variant under Monitoring
Variant under Monitoring
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_14818139
EPI_ISL_14818139
JPT’s products
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike BQ.1.1/ Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD BQ.1.1 / Omicron) Spike Receptor Binding Domain
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (Spike BQ.1.1/ Omicron) Entire Spike Protein
PepMix SARS-CoV-2 (S-RBD BQ.1.1 / Omicron) Spike Receptor Binding Domain
Mutations:
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, H0069-, V0070-, G0142D, V0213G, G0339D, R0346T, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, K0444T, L0452R, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486V, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, H0069-, V0070-, G0142D, V0213G, G0339D, R0346T, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, K0444T, L0452R, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486V, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
Omicron XBB.1.5
WHO Designation
Variant under Monitoring
Variant under Monitoring
First Publication
Enhanced transmissibility of XBB.1.5 is contributed by both strong ACE2 binding and antibody evasion
Yue et al., BioRxiv (2023)
Enhanced transmissibility of XBB.1.5 is contributed by both strong ACE2 binding and antibody evasion
Yue et al., BioRxiv (2023)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_15687648
EPI_ISL_15687648
Mutations
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, D0080A, G0142D, Y0144-, H0146Q, Q0183E, V0213E, G0252V, G0339H, R0346T, L0368I, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, V0445P, G0446S, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486P, F0490S, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, D0080A, G0142D, Y0144-, H0146Q, Q0183E, V0213E, G0252V, G0339H, R0346T, L0368I, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, V0445P, G0446S, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486P, F0490S, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
Omicron EG.5.1
WHO Designation
Variant of Interest
Variant of Interest
First Publication
Editorial: A Rapid Global Increase in COVID-19 is Due to the Emergence of the EG.5 (Eris) Subvariant of Omicron SARS-CoV-2
Parums et al., Med.Sci.Monit. (2023)
Editorial: A Rapid Global Increase in COVID-19 is Due to the Emergence of the EG.5 (Eris) Subvariant of Omicron SARS-CoV-2
Parums et al., Med.Sci.Monit. (2023)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_17432511
EPI_ISL_17432511
Mutations
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, Q0052H, D0080A, G0142D, Y0144-, H0146Q, Q0183E, V0213E, G0252V, G0339H, R0346T, L0368I, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, V0445P, G0446S, F0456L, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486P, F0490S, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
T0019I, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, A0027S, Q0052H, D0080A, G0142D, Y0144-, H0146Q, Q0183E, V0213E, G0252V, G0339H, R0346T, L0368I, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, R0408S, K0417N, N0440K, V0445P, G0446S, F0456L, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, E0484A, F0486P, F0490S, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, D0614G, H0655Y, N0679K, P0681H, N0764K, D0796Y, Q0954H, N0969K
Omicron BA.2.86
WHO Designation
Variant of Interest
Variant of Interest
First Publication
Immune Evasion, Infectivity, and Fusogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.86 and FLip Variants
Qu et al., BioRxiv (2023)
Immune Evasion, Infectivity, and Fusogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.86 and FLip Variants
Qu et al., BioRxiv (2023)
GISAID Accession ID
EPI_ISL_18096761
EPI_ISL_18096761
Mutations
+0016MPLF, T0019I, R0021T, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, S0050L, Q0052H, H0069-, V0070-, D0080A, V0127F, G0142D, Y0144-, F0157S, R0158G, Q0183E, N0211-, L0212I, V0213G, L0216F, H0245N, A0264D, I0332V, G0339H, K0356T, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, K0417N, N0440K, V0445H, G0446S, N0450D, L0452W, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, N0481K, V0483-, E0484K, F0486P, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, A0570V, D0614G, P0621S, H0655Y, I0670V, N0679K, P0681R, N0764K, D0796Y, S0939F, Q0954H, N0969K, P1143L
+0016MPLF, T0019I, R0021T, L0024-, P0025-, P0026-, S0050L, Q0052H, H0069-, V0070-, D0080A, V0127F, G0142D, Y0144-, F0157S, R0158G, Q0183E, N0211-, L0212I, V0213G, L0216F, H0245N, A0264D, I0332V, G0339H, K0356T, S0371F, S0373P, S0375F, T0376A, D0405N, K0417N, N0440K, V0445H, G0446S, N0450D, L0452W, N0460K, S0477N, T0478K, N0481K, V0483-, E0484K, F0486P, Q0498R, N0501Y, Y0505H, A0570V, D0614G, P0621S, H0655Y, I0670V, N0679K, P0681R, N0764K, D0796Y, S0939F, Q0954H, N0969K, P1143L
Loading...